Tungsten Rod Electrodes
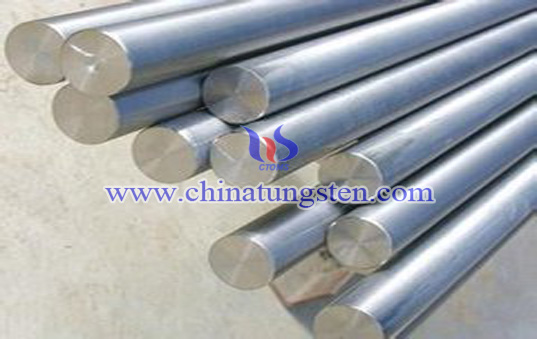
Tungsten rod electrodes shared the same properties of tungsten,tungsten rod is frequently used as electrodes in high-energy electrical equipment (such as targets in X-ray tubes and spark gaps in Tesla Coils) where other metals would vaporize or melt. The thin filaments in light bulbs are made of fine Tungsten wire. Our solid Tungsten rod are 1/8" in diameter, and 3" to 3.5" long.
How to Selecting the Right Tungsten?
Selecting the right tungsten is crucial to a successful TIG weld. You have to insure the correct tungsten is used for the type of metal you are welding, the type of technology used in your welder such as transformer or inverter, and the thickness of the metal you will need to weld. This leaves you with a variety sizes ranging from 1/16 to 1/8” and the types of tungsten’s such as the Pure Tungsten (TP), 2% Thoriated Tungsten (T2), 2% Ceriated Tungsten (TC2), and 2% Lanthanated Tungsten (TL2). Fortunately, LONGEVITY offers high quality tungsten electrodes and explains which tungsten is required for the right application. Pure Tungsten (TP) – (green tipped) - Pure tungsten readily forms a ball on the end. It is designed for use with transformer-based power sources for AC welding of aluminum. Unfortunately, LONGEVITY does not carry transformer based technology considering the size and weight of TRANSFORMER welders. Therefore, this tungsten is rarely sold buy our sales staff.
What is Tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding?
Tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding, also known as gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), is an arc welding process that uses a tungsten electrode to transmit the electric arc to the work piece. Unlike other arc welding methods, the tungsten electrode does not provide material to the weld, so a separate filler rod is needed for that purpose. Some tungsten electrodes are made with a small amount of thorium, which is a radioactive material and improves the welding qualities of the electrode.
Welding With Tungsten Tungsten has the highest melting point of all metals, so the electrode material does not melt when exposed to the high temperatures of the arc. Tungsten can be used to weld metals and specific alloys designed to have a high melting point. Even though the tungsten electrode doesn't melt during the welding process, the electrode can wear or chip over time. The electrode can be reshaped to a conical or rounded shape using a grinder.
Electrodes That Contain Thorium Thoriated tungsten electrodes are made from tungsten combined with 1 to 2 percent thorium in the form of thorium dioxide. Thoriated tungsten electrodes result in improved welding properties over pure tungsten electrodes. By using thoriated tungsten electrodes, welders find it easier to start the arc and maintain the arc, reduce weld contamination, carry a higher level of current, and achieve a longer electrode life through reduction in wear.





